Dans cet article nous allons configurer l’autoscaling d’un pool worker node pour un cluster Kubernetes déployé avec Container Service Extension 4.0.3. Cette fonctionnalité est très utile lorsque vous utilisez des HPA (Horizontal Pod Autoscaling). Elle permet de déployer des Worker node supplémentaires en fonction de la charge nécessaire pour vos applications.
Pré requis
- Un cluster Kubernetes fonctionnel déployé avec Container Service Extension
- Quelques connaissances Kubernetes
Environnement de Test
1
2
3
4
|
k get node
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
k8slorislombardi-control-plane-node-pool-njdvh Ready control-plane,master 21h v1.21.11+vmware.1
k8slorislombardi-worker-node-pool-1-69f68cc6b9-kfhz9 Ready <none> 21h v1.21.11+vmware.1
|
- 1 Master node : 2vCPU ; 4Go RAM
- 1 Worker node : 2vCPU ; 4Go RAM
Configuration HPA
Configuration Metrics
Si cela n’est pas déjà fait vous devez déployer metrics-server sur votre cluster Kubernetes
1
|
kubectl apply -f https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/metrics-server/releases/latest/download/components.yaml
|
Nous devons éditer le déploiement du metric server de la manière suivante
1
|
k edit deployments.apps metrics-server -n kube-system
|
Ajoutez l’option –kubelet-insecure-tls
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
containers:
- args:
- --cert-dir=/tmp
- --secure-port=4443
- --kubelet-preferred-address-types=ExternalIP,Hostname,InternalIP
- --kubelet-use-node-status-port
- --metric-resolution=15s
- --kubelet-insecure-tls
image: registry.k8s.io/metrics-server/metrics-server:latest
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
|
Test HPA
À partir du template suivant, nous allons configurer un déploiement et lui associer une politique HPA
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
|
# hpa-test.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: hpa-example
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: hpa-example
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: hpa-example
spec:
containers:
- name: hpa-example
image: gcr.io/google_containers/hpa-example
ports:
- name: http-port
containerPort: 80
resources:
requests:
cpu: 200m
---
apiVersion: autoscaling/v1
kind: HorizontalPodAutoscaler
metadata:
name: hpa-example-autoscaler
spec:
scaleTargetRef:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
name: hpa-example
minReplicas: 1
maxReplicas: 100
targetCPUUtilizationPercentage: 50
|
1
|
k apply -f hpa-test.yaml
|
Vérification
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
k get deployments.apps
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
hpa-example 1/1 1 1 3m21s
k get hpa
NAME REFERENCE TARGETS MINPODS MAXPODS REPLICAS AGE
hpa-example-autoscaler Deployment/hpa-example 0%/50% 1 10 1 28m
k get pod
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
hpa-example-cb54bb958-cggfp 1/1 Running 0 3m26s
nginx-nfs-example 1/1 Running 0 12h
|
Nous créons ensuite une VIP de type Load-balancer pour notre déploiement
1
|
k expose deployment hpa-example --type=LoadBalancer --port=80
|
Dans notre exemple le load-balancer assigne l’IP 172.31.7.210
1
2
3
4
|
k get svc
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
hpa-example LoadBalancer 100.68.137.181 172.31.7.210 80:32258/TCP 14s
kubernetes ClusterIP 100.64.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 20h
|
Monter en charge
Nous allons maintenant faire monter en charge notre application
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
# pod-wget.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: pod-wget
spec:
containers:
- name: alpine
image: alpine:latest
command: ['sleep', 'infinity']
|
1
2
3
4
|
k apply -f po-wget.yaml
k exec -it pod-wget -- sh
/ # while true; do wget -q -O- http://172.31.7.210;done
OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!
|
Après quelques minutes on peut voir que la fonctionnalité HPA entre en action
Saturation de la charge CPU des pod
1
2
3
|
k get hpa
NAME REFERENCE TARGETS MINPODS MAXPODS REPLICAS AGE
hpa-example-autoscaler Deployment/hpa-example 381%/50% 1 10 4 35m
|
On peut voir que l’HPA essaye de créer de nouveau POD cependant les ressources CPU du worker node sont également saturés
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
k get pod
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
hpa-example-cb54bb958-2sqpt 0/1 Pending 0 67s
hpa-example-cb54bb958-44k4x 0/1 Pending 0 52s
hpa-example-cb54bb958-6vd5l 0/1 Pending 0 52s
hpa-example-cb54bb958-82fb4 0/1 Pending 0 82s
hpa-example-cb54bb958-dpwwc 1/1 Running 0 40m
hpa-example-cb54bb958-ltb96 0/1 Pending 0 67s
hpa-example-cb54bb958-nsd54 0/1 Pending 0 67s
hpa-example-cb54bb958-w74fx 0/1 Pending 0 82s
hpa-example-cb54bb958-wz54z 1/1 Running 0 82s
hpa-example-cb54bb958-zrgw4 0/1 Pending 0 67s
k describe pod hpa-example-cb54bb958-2sqp
Warning FailedScheduling 11s (x3 over 82s) default-scheduler 0/2 nodes are available: 1 Insufficient cpu, 1 node(s) had taint {node-role.kubernetes.io/master: }, that the pod didn't tolerate.
|
Activation de l’autoscaling
Cette fonctionnalité n’est pas activée par défaut sur les cluster Kubernetes déployés par CSE et n’est pas encore implémentée par VMware. Voici une méthode pas à pas pour configurer cette fonctionnalité en attendant que celle-ci soit intégrée dans la road-map de développement.
Préparation des composants nécessaires
Identifier le namespace admin de votre cluster. Dans cet exemple mon cluster est nommé k8slorislombardi
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
k get namespaces
NAME STATUS AGE
capi-kubeadm-bootstrap-system Active 21h
capi-kubeadm-control-plane-system Active 21h
capi-system Active 21h
capvcd-system Active 21h
cert-manager Active 21h
default Active 21h
hpa-test Active 93m
k8slorislombardi-ns Active 21h
kube-node-lease Active 21h
kube-public Active 21h
kube-system Active 21h
nfs-csi Active 15h
rdeprojector-system Active 21h
tanzu-package-repo-global Active 21h
tkg-system Active 21h
tkg-system-public Active 21h
tkr-system Active 21h
|
Le namespace “admin” de ce cluster est donc k8slorislombardi-ns
Toutes les étapes ci-dessous sont à réaliser dans le namespace “admin” : k8slorislombardi-ns
- Créer un pod temporaire et un PVC contenant notre kubeconfig
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
|
#autoscale-config.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
annotations:
volume.beta.kubernetes.io/storage-provisioner: named-disk.csi.cloud-director.vmware.com
name: pvc-autoscaler
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 10Mi
storageClassName: default-storage-class-1
volumeMode: Filesystem
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: pod-temporaire
spec:
containers:
- name: alpine
image: alpine:latest
command: ['sleep', 'infinity']
volumeMounts:
- name: pvc-autoscaler
mountPath: /data
volumes:
- name: pvc-autoscaler
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: pvc-autoscaler
|
Application et vérification
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
k apply -f autoscale-config.yaml
k get pvc
NAME STATUS VOLUME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES STORAGECLASS AGE
pvc-autoscaler Bound pvc-775762d2-34e7-4854-823d-8f757d94437e 10Mi RWO default-storage-class-1 3m8s
k get pod
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod-temporaire 1/1 Running 0 2m57s
|
- Copie du fichier kubeconfig
1
2
3
4
5
|
k exec -it pod-temporaire -- sh
/ #
/ # cd /data
/data #
vi config
|
Copiez le contenu de votre kubeconfig dans un nouveau fichier nommé config
Vous pouvez ensuite supprimer le pod-temporaire
1
|
k delete pod pod-temporaire
|
- Configurer les ressources hardware du pool worker-node
1
2
3
4
5
|
k get machinedeployments.cluster.x-k8s.io
NAME CLUSTER REPLICAS READY UPDATED UNAVAILABLE PHASE AGE VERSION
k8slorislombardi-worker-node-pool-1 k8slorislombardi 1 1 1 0 Running 23h v1.21.11+vmware.1
k edit machinedeployments.cluster.x-k8s.io k8slorislombardi-worker-node-pool-1
|
Nous modifions les paramètres de la propriété machinedeployments.cluster.x-k8s.io afin de définir :
- Le nombre maximum et minimum de Worker-node présent dans le pool
- Les ressources hardware des worker-node à déployer
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
apiVersion: cluster.x-k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: MachineDeployment
metadata:
annotations:
kubectl.kubernetes.io/last-applied-configuration: |
{"apiVersion":"cluster.x-k8s.io/v1beta1","kind":"MachineDeployment","metadata":{"annotations":{},"creationTimestamp":null,"name":"k8slorislombardi-worker-node-pool-1","namespace":"k8slorislombardi-ns"},"spec":{"clusterName":"k8slorislombardi","replicas":1,"selector":{},"template":{"metadata":{},"spec":{"bootstrap":{"configRef":{"apiVersion":"bootstrap.cluster.x-k8s.io/v1beta1","kind":"KubeadmConfigTemplate","name":"k8slorislombardi-worker-node-pool-1","namespace":"k8slorislombardi-ns"}},"clusterName":"k8slorislombardi","infrastructureRef":{"apiVersion":"infrastructure.cluster.x-k8s.io/v1beta1","kind":"VCDMachineTemplate","name":"k8slorislombardi-worker-node-pool-1","namespace":"k8slorislombardi-ns"},"version":"v1.21.11+vmware.1"}}},"status":{"availableReplicas":0,"readyReplicas":0,"replicas":0,"unavailableReplicas":0,"updatedReplicas":0}}
cluster.x-k8s.io/cluster-api-autoscaler-node-group-max-size: "5"
cluster.x-k8s.io/cluster-api-autoscaler-node-group-min-size: "1"
capacity.cluster-autoscaler.kubernetes.io/memory: "4"
capacity.cluster-autoscaler.kubernetes.io/cpu: "2"
capacity.cluster-autoscaler.kubernetes.io/ephemeral-disk: "20Gi"
capacity.cluster-autoscaler.kubernetes.io/maxPods: "200"
machinedeployment.clusters.x-k8s.io/revision: "1"
|
Déploiement de l’autoscaler
Nous utilisons le yaml suivant pour qu’il utilise le PVC précédemment créé afin de récupérer le kubeconfig.
Veillez à bien remplacer k8slorislombardi et k8slorislombardi-ns par les paramètres de votre cluster
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
|
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: cluster-autoscaler
namespace: k8slorislombardi-ns
labels:
app: cluster-autoscaler
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: cluster-autoscaler
replicas: 1
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: cluster-autoscaler
spec:
containers:
- image: us.gcr.io/k8s-artifacts-prod/autoscaling/cluster-autoscaler:v1.20.0
name: cluster-autoscaler
command:
- /cluster-autoscaler
args:
- --cloud-provider=clusterapi
- --kubeconfig=/data/config
- --cloud-config=/data/config
- --node-group-auto-discovery=clusterapi:clusterName=k8slorislombardi
- --namespace=k8slorislombardi-ns
- --node-group-auto-discovery=clusterapi:namespace=default
volumeMounts:
- name: pvc-autoscaler
mountPath: /data
volumes:
- name: pvc-autoscaler
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: pvc-autoscaler
serviceAccountName: cluster-autoscaler
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 10
---
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: cluster-autoscaler-workload
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: cluster-autoscaler-workload
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: cluster-autoscaler
namespace: k8slorislombardi-ns
---
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: cluster-autoscaler-management
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: cluster-autoscaler-management
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: cluster-autoscaler
namespace: k8slorislombardi-ns
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: cluster-autoscaler
namespace: k8slorislombardi-ns
---
kind: ClusterRole
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: cluster-autoscaler-workload
rules:
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- namespaces
- persistentvolumeclaims
- persistentvolumes
- pods
- replicationcontrollers
- services
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- nodes
verbs:
- get
- list
- update
- watch
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- pods/eviction
verbs:
- create
- apiGroups:
- policy
resources:
- poddisruptionbudgets
verbs:
- list
- watch
- apiGroups:
- storage.k8s.io
resources:
- csinodes
- storageclasses
- csidrivers
- csistoragecapacities
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
- apiGroups:
- batch
resources:
- jobs
verbs:
- list
- watch
- apiGroups:
- apps
resources:
- daemonsets
- replicasets
- statefulsets
verbs:
- list
- watch
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- events
verbs:
- create
- patch
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- configmaps
verbs:
- create
- delete
- get
- update
- apiGroups:
- coordination.k8s.io
resources:
- leases
verbs:
- create
- get
- update
---
kind: ClusterRole
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: cluster-autoscaler-management
rules:
- apiGroups:
- cluster.x-k8s.io
resources:
- machinedeployments
- machinedeployments/scale
- machines
- machinesets
verbs:
- get
- list
- update
- watch
|
Vérification
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
k apply -f .\autoscale.yaml
deployment.apps/cluster-autoscaler created
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/cluster-autoscaler-workload created
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/cluster-autoscaler-management created
serviceaccount/cluster-autoscaler created
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/cluster-autoscaler-workload created
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/cluster-autoscaler-management created
k get pod
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
cluster-autoscaler-79c5cb9df6-gqlfd 1/1 Running 0 29s
|
Configuration rdeprojector
Par défaut Cloud director vérifie en permanence la configuration de votre custer Kubernetes via contrôleur rdeprojector. Ce contrôleur permet également d’ajouter ou supprimer des worker node à partir de l’interface graphique de cloud director
Le contrôleur rdeprojector ne peut pas fonctionner avec la configuration autoscale que nous venons de déployer. En effet l’autoscaler va déployer un nouveau worker-node, rdeprojector va détecter une incohérence et donc supprimer le nouveau worker-node. A noter qu’il ne sera plus possible de modifier la configuration de votre cluster à partir de l’interface graphique de Cloud Director.
1
|
k edit deployments.apps rdeprojector-controller-manager -n rdeprojector-system
|
Modifier le nombre de replicas à 0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
spec:
progressDeadlineSeconds: 600
replicas: 0
revisionHistoryLimit: 10
selector:
matchLabels:
control-plane: controller-manager
|
Test Autoscaling
1
2
3
4
|
k apply -f po-wget.yaml
k exec -it pod-wget -- sh
/ # while true; do wget -q -O- http://172.31.7.210;done
OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!
|
Comme vu précédemment quelques minutes plus tard le CPU des Pod et du Worker node sont saturés
1
2
3
|
k get hpa -n default
NAME REFERENCE TARGETS MINPODS MAXPODS REPLICAS AGE
hpa-example-autoscaler Deployment/hpa-example 122%/50% 1 10 8 3h17m
|
L’autoscaler entre en action et déploiement un nouveau Worker-node
1
2
3
|
k get machinedeployments.cluster.x-k8s.io
NAME CLUSTER REPLICAS READY UPDATED UNAVAILABLE PHASE AGE VERSION
k8slorislombardi-worker-node-pool-1 k8slorislombardi 2 1 2 1 ScalingUp 24h v1.21.11+vmware.1
|
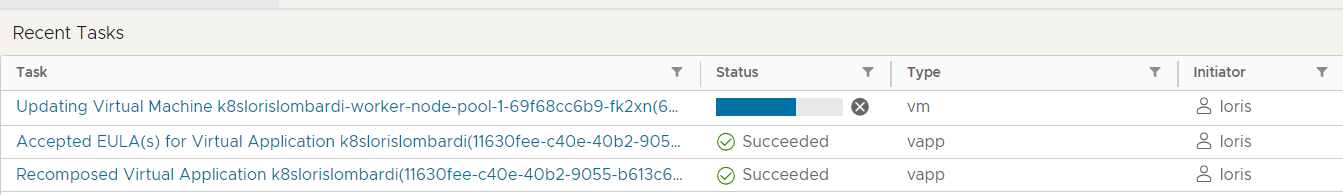
Intégration automatique du nouveau Worker-node
1
2
3
4
5
|
k get node
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
k8slorislombardi-control-plane-node-pool-njdvh Ready control-plane,master 24h v1.21.11+vmware.1
k8slorislombardi-worker-node-pool-1-69f68cc6b9-fk2xn NotReady <none> 3s v1.21.11+vmware.1
k8slorislombardi-worker-node-pool-1-69f68cc6b9-kfhz9 Ready <none> 24h v1.21.11+vmware.1
|
Le nouveau Worker est actif
1
2
3
4
5
|
k get node
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
k8slorislombardi-control-plane-node-pool-njdvh Ready control-plane,master 24h v1.21.11+vmware.1
k8slorislombardi-worker-node-pool-1-69f68cc6b9-fk2xn Ready <none> 42s v1.21.11+vmware.1
k8slorislombardi-worker-node-pool-1-69f68cc6b9-kfhz9 Ready <none> 24h v1.21.11+vmware.1
|
Des pod supplémentaires sont déployés
1
2
3
|
k get deployments.apps
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
hpa-example 10/10 10 10 3h29m
|
Source : [cluster-autoscaler]https://github.com/kubernetes/autoscaler/tree/master/cluster-autoscaler)


